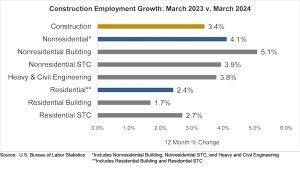
The construction industry added 39,000 jobs on net in March, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data released today by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. On a year-over-year basis, industry employment has expanded by 270,000 jobs, an increase of 3.4%.
Nonresidential construction employment increased by 24,600 positions on net, with growth in all three subcategories. Nonresidential specialty trade added the most jobs, increasing by 16,300 positions. Heavy and civil engineering and nonresidential building added 6,000 and 2,300 jobs, respectively.
The construction unemployment rate fell to 5.4% in March. Unemployment across all industries declined from 3.9% in February to 3.8% last month.
“Today’s release was a blockbuster jobs report and indicates that recession is not arriving anytime soon,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “The 39,000 jobs added by the nation’s construction segment was roughly twice the monthly growth observed over the past year. If one focuses purely on nonresidential construction, monthly job growth was nearly 80% faster than the one-year average.
“Structural transformations in the economy, including replenished domestic supply chains, expanded data center demand and augmented infrastructure, are making it difficult for many project owners to wait for lower construction delivery costs,” said Basu. “Despite the effects of worker shortages, still-elevated materials prices, newly emerging supply chain issues and the high cost of project financing, both privately and publicly financed segments produced substantial employment growth in March. This comports with ABC’s Construction Confidence Index, which shows that a large share of contractors intend to grow their staffing levels over the next six months.
“As always, the jobs report was not completely positive,” said Basu. “Those in search of lower inflation and interest rates will not be comforted by this release. While economywide year-over-year wage growth softened to 4.1% in March, the monthly wage growth figure suggested a pace of compensation growth that will render it difficult for the Federal Reserve to substantially reduce interest rates in 2024. The notion that interest rates will remain higher for longer remains firmly in place, which means that project financing costs will likely be an ongoing issue for construction demand, especially in privately financed segments, for the foreseeable future.”